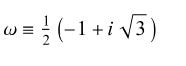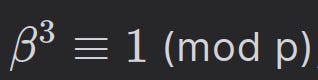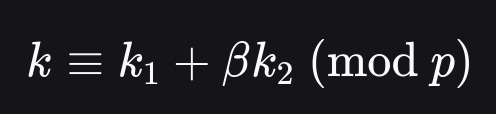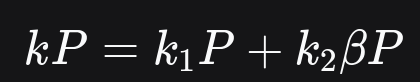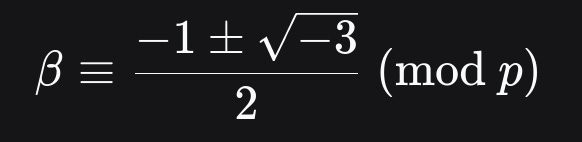Quick Intro
LeetArxiv is a successor to Papers With Code after the latter shutdown. There’s free GPU credits at the end.
Here’s the Polymarket bet on touching Satoshi’s wallet..
Quick Summary
The paper introduces the GLV endomorphism for fast scalar multiplication on elliptic curves where p mod 1 = 3
Here is 12 months of Perplexity Pro on us.
Here’s 20 dollars to send money abroad.
Here are some free gpu credits :)
Code is available on Google Colab and GitHub.
1.0 Paper Introduction
The 2001 paper Faster Point Multiplication on Elliptic Curves with Efficient Endomorphisms (Gallant, Lambert & Vanstone, 2001)1 demonstrates efficient scalar multiplication on elliptic curves whose field characteristic modulo 3 is 1.
*Here’s our Programmer’s Introduction to Elliptic Curves.
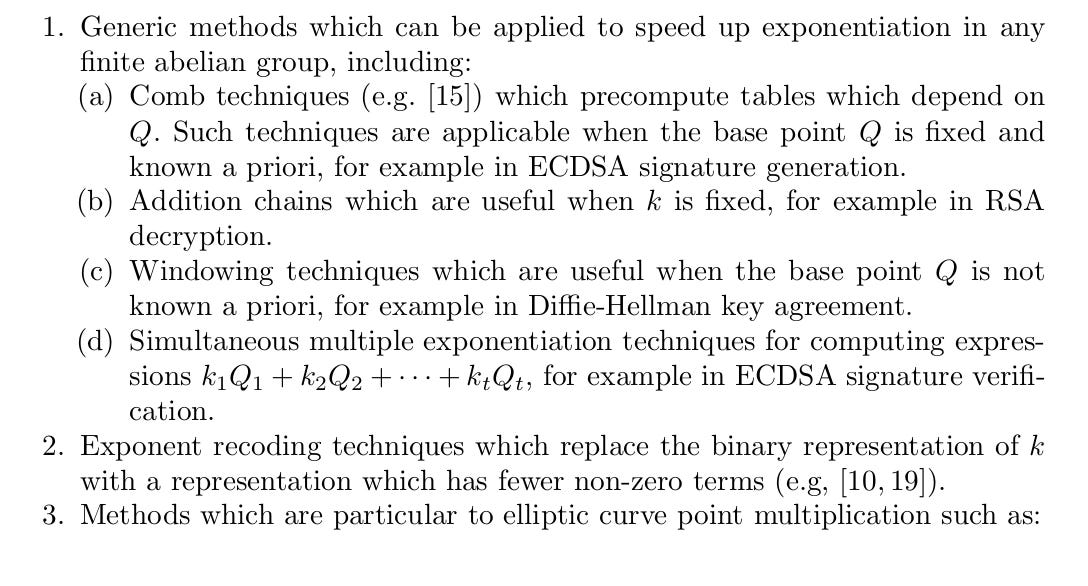
The authors acknowledge lots of different techniques to speed up arithmetic in a finite field.
Their paper introduces the GLV endomorphism : a method to halve the point operations needed for scalar multiplication on an elliptic curve.
Important Definitions
Koblitz curve over prime field - Elliptic curves of the form y2 = x3 + b modulo p where p ≡ 1 mod 3 (Wu & Xu, 2023)2.
Endomorphism - a homomorphism from an object to itself (Marsh, 2018)3
Endomorphisms are like wormholes that permit you jump around the universe super fast lol.
Eisenstein integers - complex numbers of the form
a+bwwhereaandbare normal integers andwis a cube root of unity (Weisstein, 2025)4:
2.0 GLV Endomorphism
The GLV endomorphism is a math trick for reducing the number of point doublings by half during scalar multiplication.
2.1 How does the GLV endomorphism work?
Our elliptic curve has the form y2 = x3 + b.
If we multiply x by β then our new point is y2 = (βx)3 + b.
But we know (β)3 ≡ 1 mod p.
So we can quickly move around the elliptic curve by multiplying our x coordinates by a root of unity.
2.2 GLV Algorithm
For a scalar k and an elliptic curve point P we can find kP by the GLV endomorphism like this (Drouyang, 2023)5:
Find a cube root of unity modulo p:
Write the scalar k as a sum of the factors of the cube root:
Now, we can find kP by performing addition like this:
Note that finding (βP) is done by multiplying the x coordinate of P by Beta.
Also note that k_1 and k_2 are half the size of k.
3.0 Coding Guide
We covered the math of Eisenstein integers earlier. So I’ll gloss over the fine points.
3.1 Cube Roots of Unity
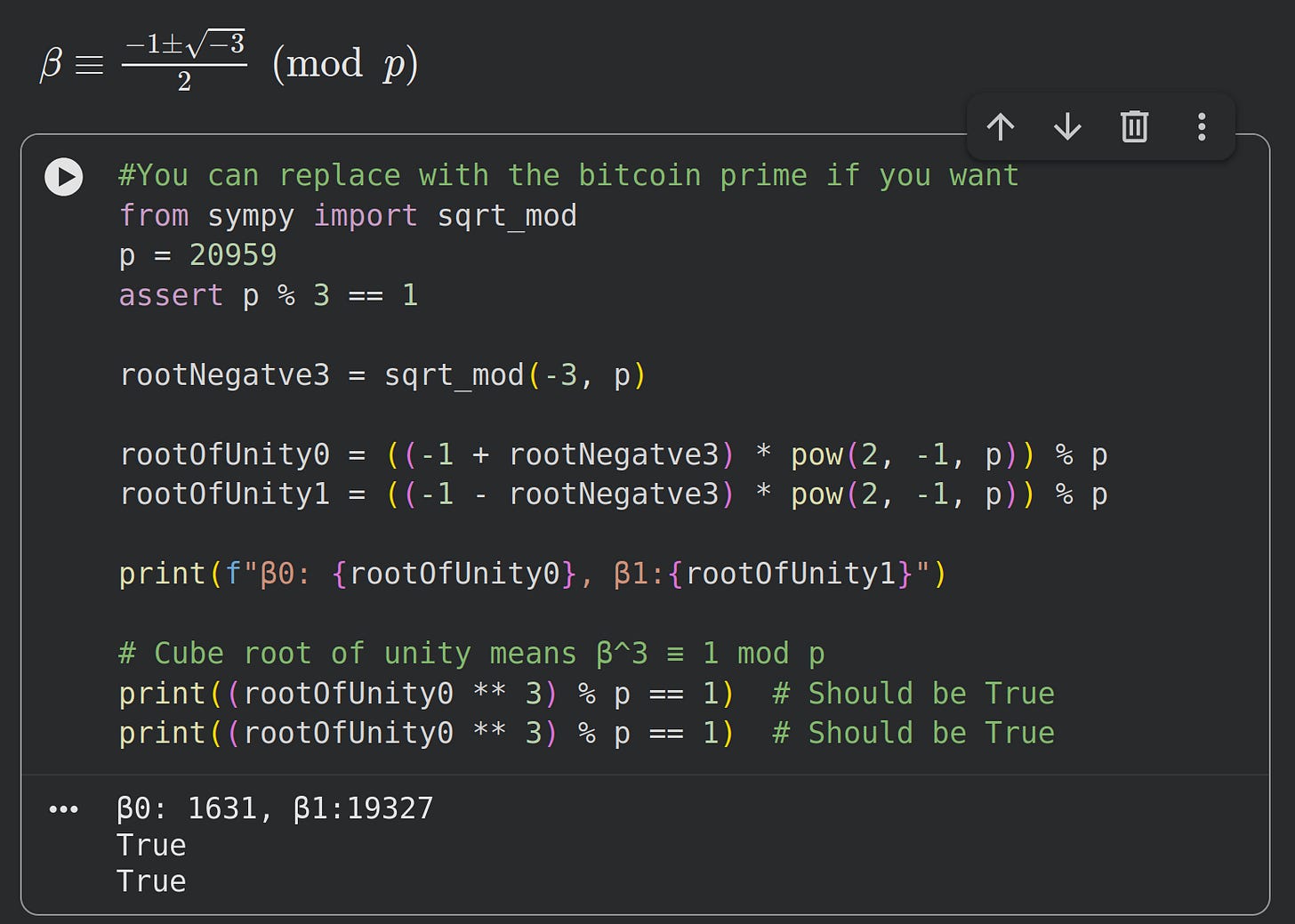
We use Eisenstein integers to find cube roots of unity for curves where p ≡ 1 mod 3:
In Python this resembles:
3.2 Splitting k into Half-sized Parts
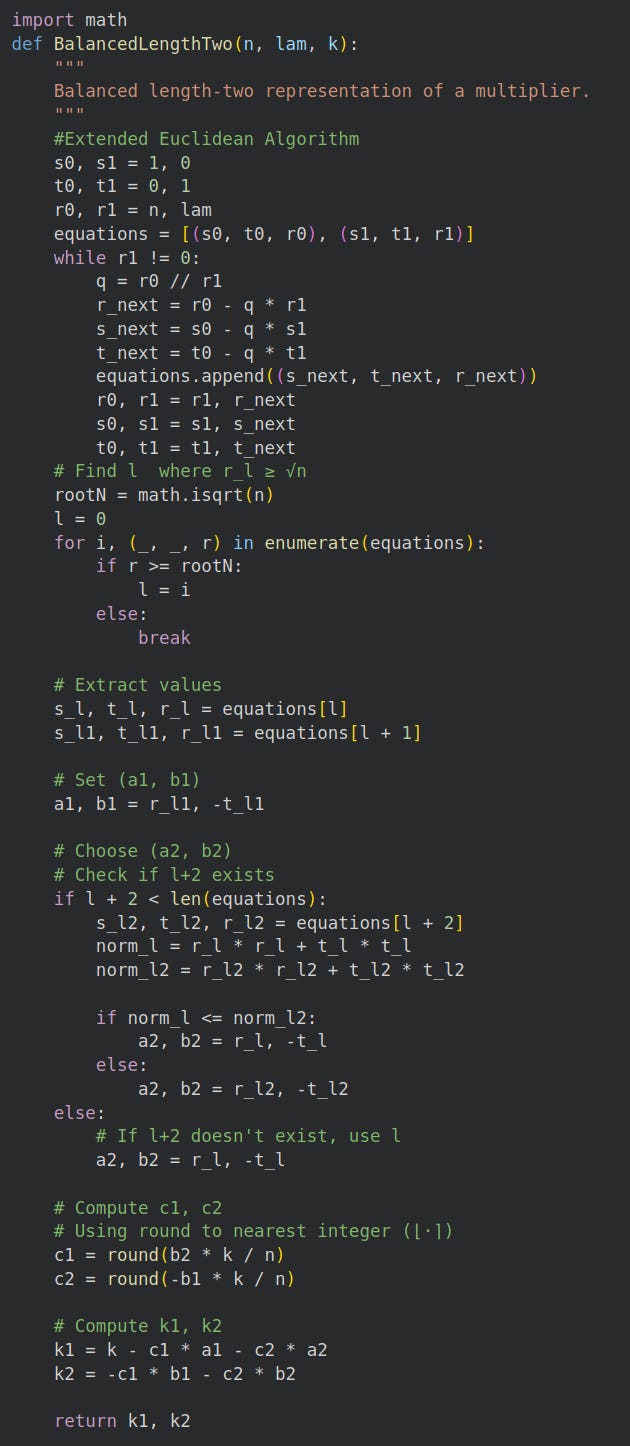
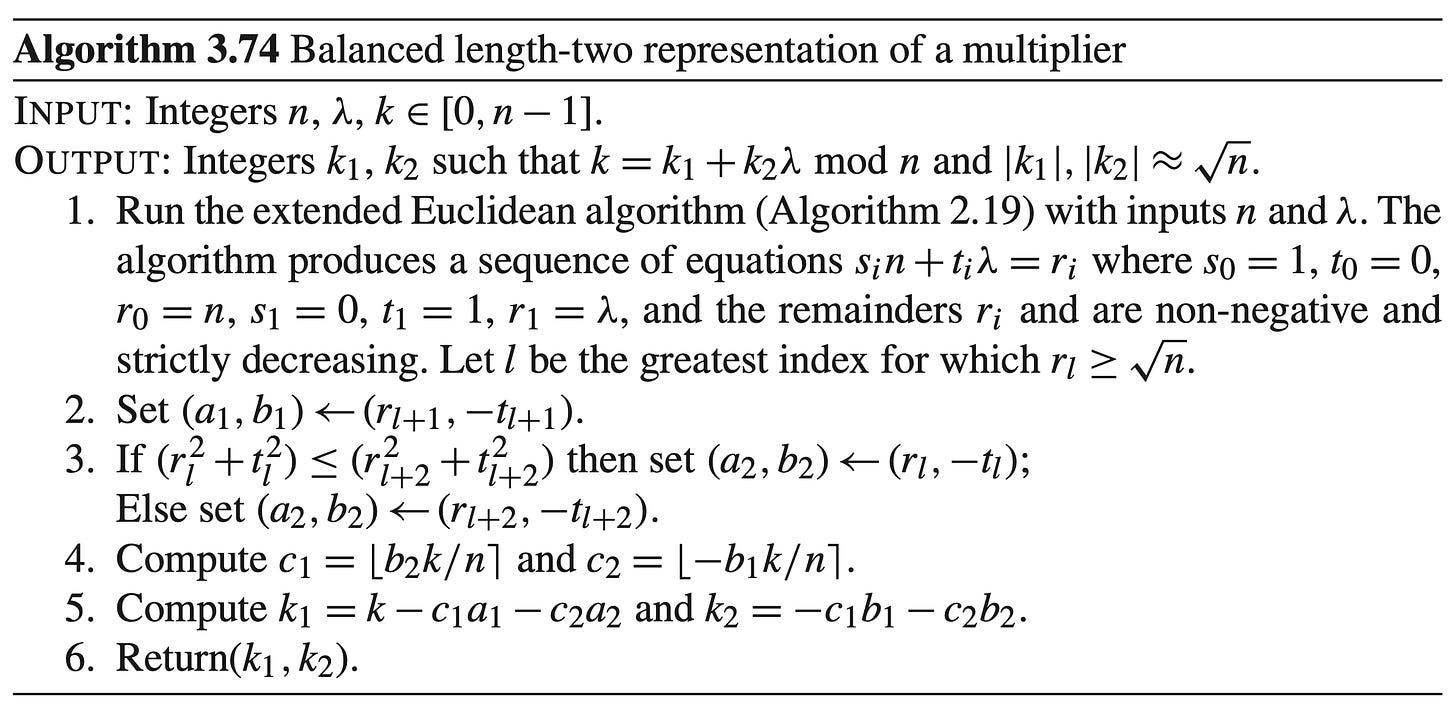
We use the balanced length-two representation of a multiplier algorithm:
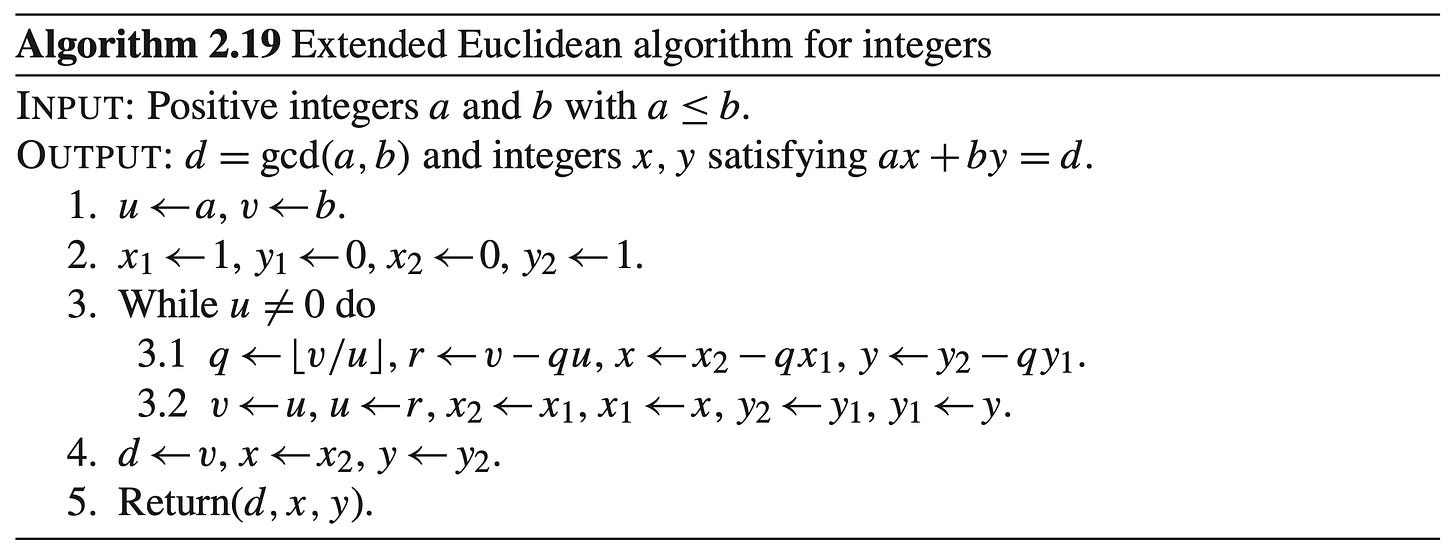
and the Extended Euclidean algorithm is:
In Python, this resembles:
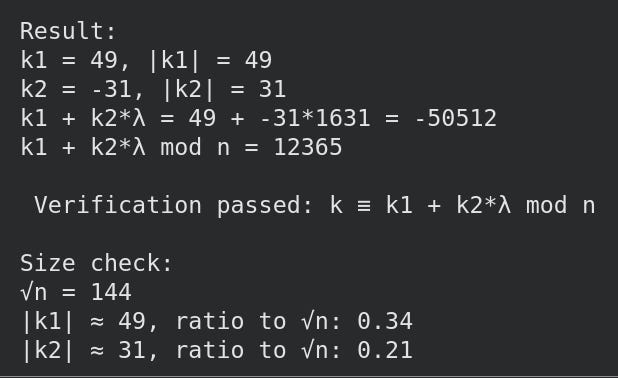
and we can verify it works:
Now we can use the GLV endomorphism in the elliptic curve library we wrote here.
4.0 Further Reading
Here are some free gpu credits if you made it this far.
References
Gallant, R. P., Lambert, R. J., & Vanstone, S. A. (2001). Faster point multiplication on elliptic curves with efficient endomorphisms. In J. Kilian (Ed.), Advances in Cryptology — CRYPTO 2001 (pp. 190–200). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44647-8_11
Marsh, A. (2018). Difference between epimorphism, isomorphism, endomorphism and automorphism (with examples). Mathematics Stack Exchange. Retrieved from https://math.stackexchange.com/q/2622567