Generators for Certain Alternating Groups With Applications to Cryptography
Step-by-Step Coding Implementation of Coppersmith and Grossman's 1975 paper

Quick intro
LeetArxiv is Leetcode for implementing Arxiv and other research papers.
This paper1 features in both our Reversible Computing Series and Cryptography Series :
Reversible Computing Series
Logical Reversibilty of Computation : This paper laid the foundation for Quantum, Thermodynamic and Catalytic computing.
Generators for Certain Alternating Groups With Applications to Cryptography(we are here) - Introduces the idea of symmetric groups for Catalytic computers and proves that all boolean functions can be transparently computed.
Cryptography Series
Lehmer’s Continued Factorization Algorithm : This paper introduces a factorization algorithm using Continued Fractions.
Asymptotically Fast Factorization of Integers : This paper introduces Dixon’s algorithm for integer factorization.
Generators for Certain Alternating Groups With Applications to Cryptography(we are here) - Proves that simple binary permutations make great, cryptographically secure ciphers.
If you’re coding along then here’s the gist.
1.0 Introduction
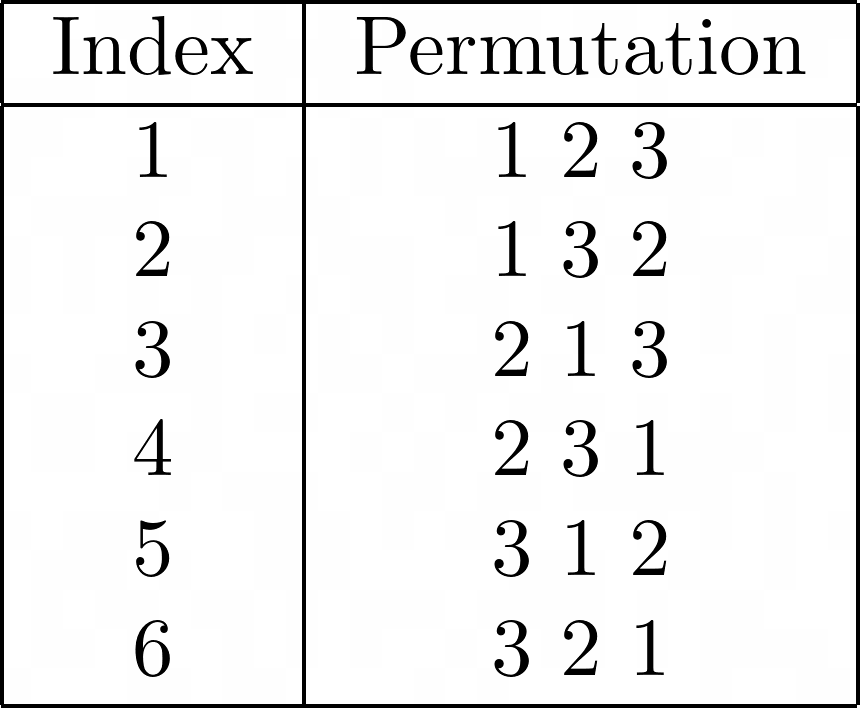
In group theory, the symmetric group, denoted by Sn, is the set of all permutations. The size* of the symmetric group is n!
*The word, ‘order’ means the size of the group while ‘!’ is the factorial.
For example, the symmetric group S3, has an order of 3! = 6 and is the set of all permutations of {1,2,3}
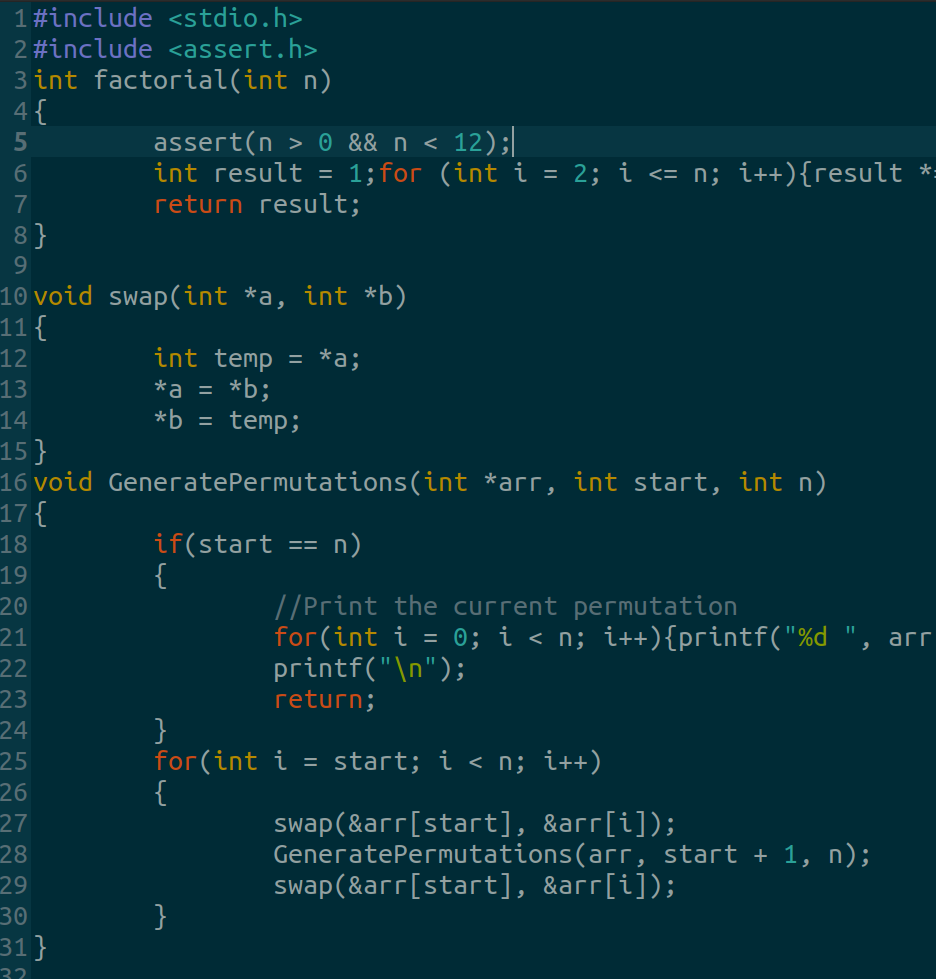
In C, we can use simple recursion to generate the symmetric group of n.
*Note that 12! is the largest value an int takes.
The authors also introduce the concept of basic functions : subsets of the symmetric group of n whose members are part of the set of simple reversible transformations.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to LeetArxiv to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.